Description:Rabbit polyclonal antibody to p300Immunogen:KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the N-term region of human p300. The exact sequence is proprietary.Purification:The antibody was purified by immunogen affinity chromatography.Clonality:PolyclonalForm:Liquid in 0.42% Potassium phosphate, 0.87% Sodium chloride, pH 7.3, 30% glycerol, and 0.01% sodium azide.Dilution:WB (1/500 - 1/1000), IH (1/50 - 1/100), IF/IC (1/50 - 1/200)Gene Symbol:EP300Alternative Names:P300; Histone acetyltransferase p300; p300 HAT; E1A-associated protein p300
Entrez Gene (Human):
2033;
Entrez Gene (Mouse):
328572;
SwissProt (Human):
Q09472;
SwissProt (Mouse):
B2RWS6;
Storage/Stability:Shipped at 4°C. Upon delivery aliquot and store at -20°C for one year. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
-
 Western blot analysis of p300 expression in C6 (A), CT26 (B) whole cell lysates. (Predicted band size: 264 kD; Observed band size: 264 kD)
Western blot analysis of p300 expression in C6 (A), CT26 (B) whole cell lysates. (Predicted band size: 264 kD; Observed band size: 264 kD) -
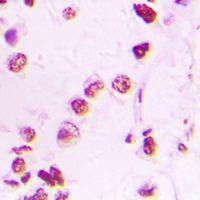 Immunohistochemical analysis of p300 staining in human lung cancer formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue section. The section was pre-treated using heat mediated antigen retrieval with sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0). The section was then incubated with the antibody at room temperature and detected using an HRP conjugated compact polymer system. DAB was used as the chromogen. The section was then counterstained with haematoxylin and mounted with DPX.
Immunohistochemical analysis of p300 staining in human lung cancer formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue section. The section was pre-treated using heat mediated antigen retrieval with sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0). The section was then incubated with the antibody at room temperature and detected using an HRP conjugated compact polymer system. DAB was used as the chromogen. The section was then counterstained with haematoxylin and mounted with DPX. -
 Immunofluorescent analysis of p300 staining in A2780 cells. Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with the primary antibody in 3% BSA-PBS and incubated overnight at 4 °C in a hidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a AF488-conjugated secondary antibody (green) in PBS at room temperature in the dark. Phalloidin - AF594 was used to stain Actin filaments (red). DAPI was used to stain the cell nuclei (blue).
Immunofluorescent analysis of p300 staining in A2780 cells. Formalin-fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 minutes and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with the primary antibody in 3% BSA-PBS and incubated overnight at 4 °C in a hidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a AF488-conjugated secondary antibody (green) in PBS at room temperature in the dark. Phalloidin - AF594 was used to stain Actin filaments (red). DAPI was used to stain the cell nuclei (blue).
CBP/p300-mediated acetylation of histone H3 on lysine 56
Progesterone Receptor Coregulators as Factors Supporting the Function of the Corpus Luteum in Cows
Steroid Receptor Coregulators Can Modulate the Action of Progesterone Receptor during the Estrous Cycle in Cow Endometrium
Luteotropic and Luteolytic Factors Modulate the Expression of Nuclear Receptor Coregulators in Bovine Luteal Cells Independently of Histone Acetyltransferase and Histone Deacetylase Activities


 Datasheet
Datasheet MSDS
MSDS